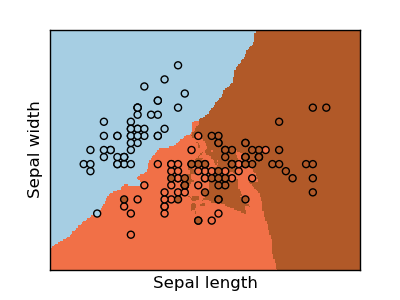
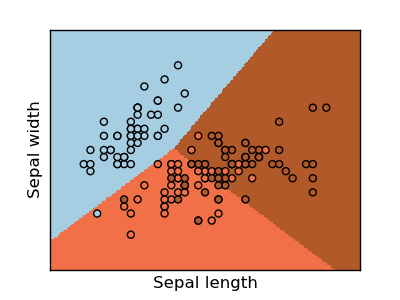
Classifiers Comparison¶
A Comparison of a K-nearest-neighbours, Logistic Regression and a Linear SVC classifying the iris dataset.
Python source code: plot_iris_classifiers.py
print __doc__
# Code source: Gael Varoqueux
# Modified for Documentation merge by Jaques Grobler
# License: BSD
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl
from sklearn import neighbors, datasets, linear_model, svm
# import some data to play with
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, :2] # we only take the first two features.
Y = iris.target
h = .02 # step size in the mesh
classifiers = dict(
knn=neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier(),
logistic=linear_model.LogisticRegression(C=1e5),
svm=svm.LinearSVC(C=1e5, loss='l1'),
)
fignum = 1
# we create an instance of Neighbours Classifier and fit the data.
for name, clf in classifiers.iteritems():
clf.fit(X, Y)
# Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will asign a color to each
# point in the mesh [x_min, m_max]x[y_min, y_max].
x_min, x_max = X[:,0].min() - .5, X[:,0].max() + .5
y_min, y_max = X[:,1].min() - .5, X[:,1].max() + .5
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
# Put the result into a color plot
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
pl.figure(fignum, figsize=(4, 3))
pl.set_cmap(pl.cm.Paired)
pl.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z)
# Plot also the training points
pl.scatter(X[:,0], X[:,1], c=Y)
pl.xlabel('Sepal length')
pl.ylabel('Sepal width')
pl.xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
pl.ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
pl.xticks(())
pl.yticks(())
fignum += 1
pl.show()